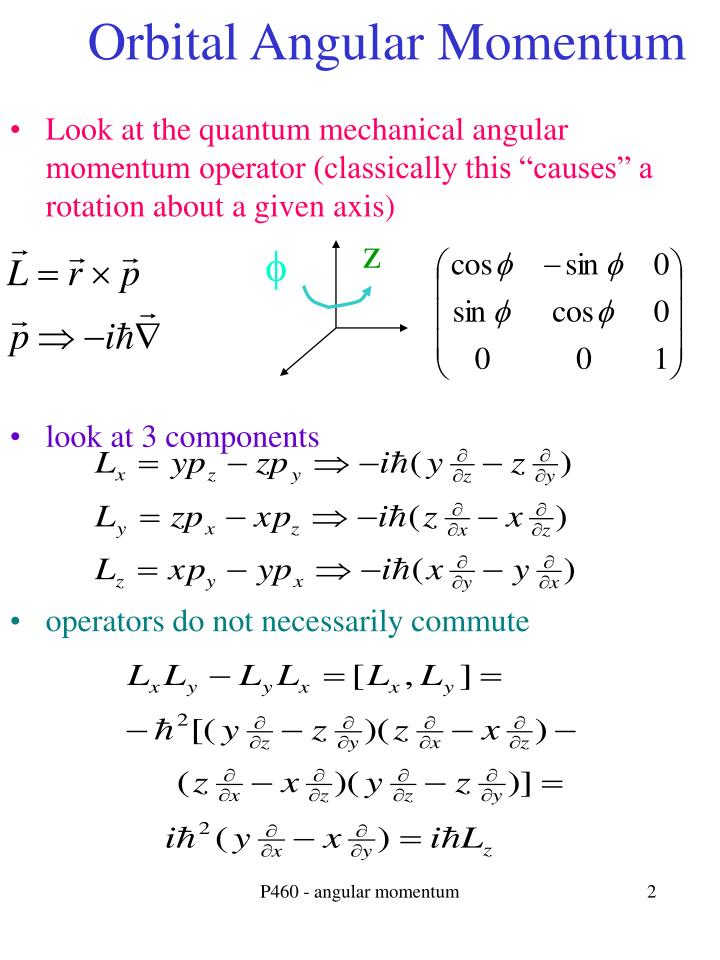
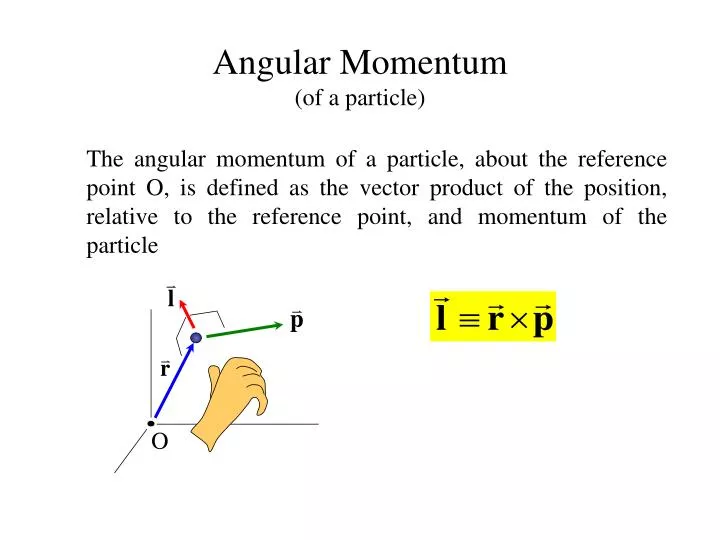
Is defined as the cross-product of the position vector lr and the momentum vector pl. 11 In cartesian components this equation reads L.
How Does Mass Affect Angular Momentum Quora
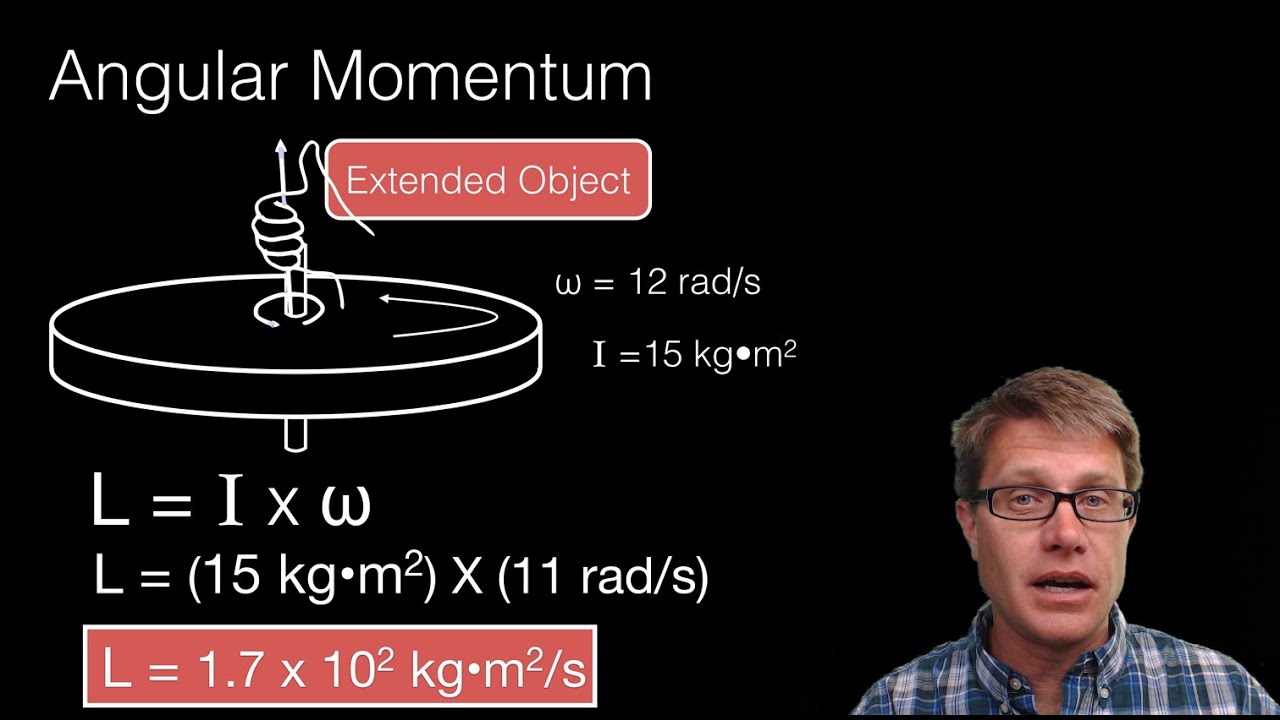
Similarly we can derive the x- and y-components as L x ih sin cot cos.

Angular momentum x component. Angular Momentum in Spherical Coordinates In this appendix we will show how to derive the expressions of the gradient v the Laplacian v2 and the components of the orbital angular momentum in spherical coordinates. Operator and the difierence of operators is another operator we expect the components of angular momentum to be operators. These are the components.
In Cartesian coordinates the three operators for the orbital angular momentum components can be written as. Note that the quantum number m means the z-component of angular momentum in units of hbar. Here v perp is the component of the particles velocity perpendicular to the axis of rotation.
End Solution Copyright c 2012 Edward J. For a quantum system the angular momentum is an observable we canmeasurethe angularmomentum of a particle in a given quantum state. The amazing fact is that the different components of angular momentum do not commute.
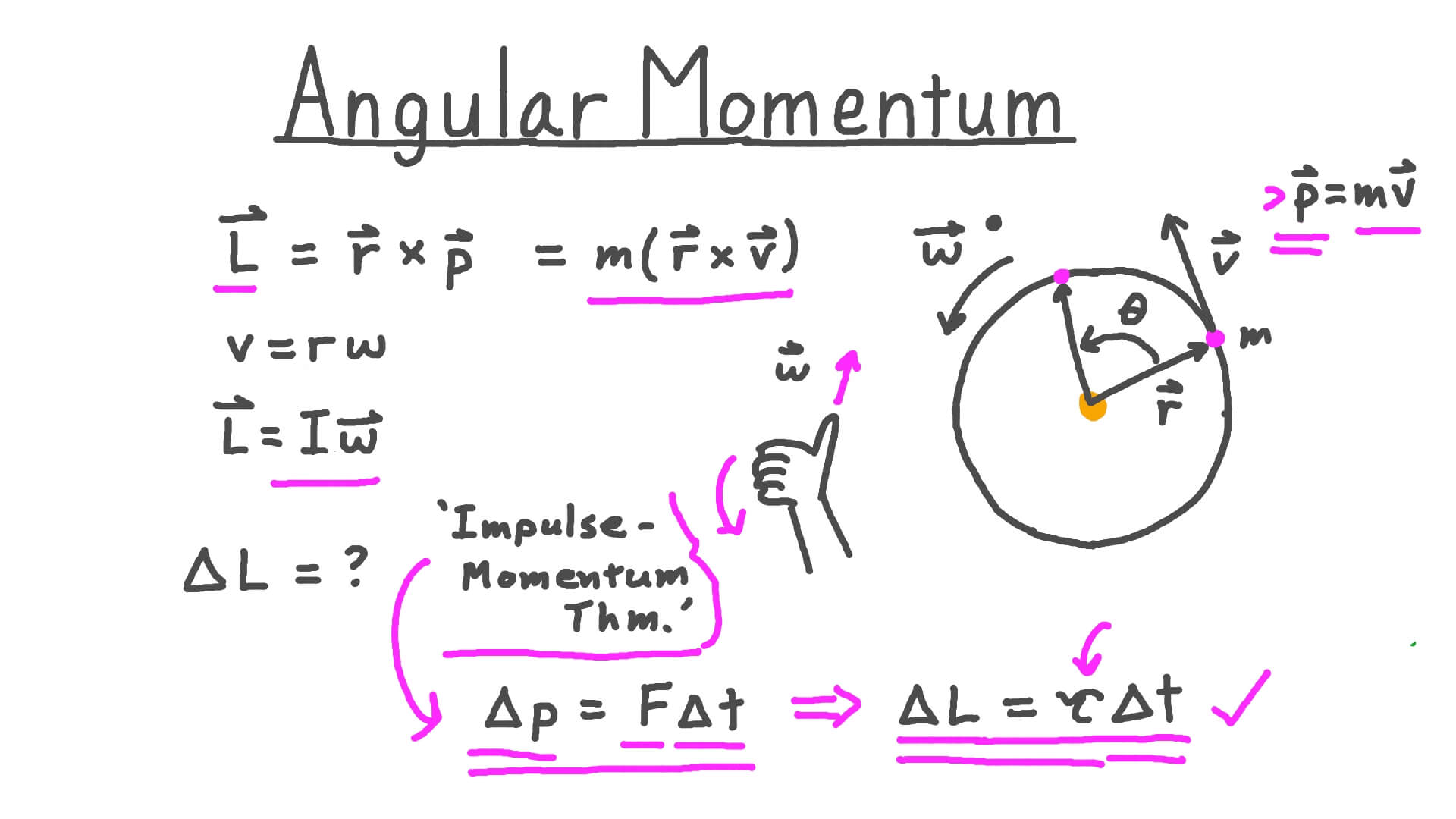
The uncertainty relation becomes LxLy h 2ll 1l22 h2l2 hLxLyi2 hihL zi h2l2. Classically the angular momentum vector L. The direction of the angular momentum is given by the right-hand rule.
Angular momentum is the vector sum of the components. From the de nition of the raising and lowering operators L L x iLy it is straightforward to obtain L i he i i cot. In Cartesian coordinates the three operators for the orbital angular momentum components can be written as 635 L x i ℏ y z z y.
For the remainder of this Appendix we will study eigenfunction-eigenvalue relationships that are characteristic of all angular momenta and which are consequences of the commutation relations among the angular momentum vectors three components. To demonstrate that this association of m with the z-component of angular momentum is indeed correct we need to write an operator for the z-component of angular momentum. L x i ℏ y z z y L y i ℏ z x x z L z i ℏ x y y x These can be transforming to operators in standard spherical polar coordinates x.
In this case the angular momentum components in the xand ydirections have the mini-mum possible uncertainty product. 51 Orbital Angular Momentum of One or More Particles The classical orbital angular momentum of a single particle about a given origin is given by the cross product r p 51 of its position and momentum vectors. L y ZP x XP z.
We know the quantum operators of position and momentum and can just substitute them in to find the angular momentum quantum operator. Angular momentum is a vector. Angular momentum square In order to obtain the square of angular momentum operator in the spherical coordinates consider L x 2 L x.
1 Orbital angular momentum and central potentials. As it turns out the angular momentum is completely described in terms of the position and momentum in the x y z directions of the particle. The total angular momentum of a collection of individual angular momenta is defined component-by-component as follows.
In other words we are going to assume that the above equations specify the angular momentum operators in terms of the position and linear momentum operators. L lr pl. Components of Lx and Ly which average to 0 but have some spread around the average.
The magnitude of the orbital angular momentum of the particle is L mrv perp mr 2 ω. The sum of operators is another operator so angular momentum is an operator. According to the postulates that wehave spelled out in previous lectures we need to associate to each observable a Hermiteanoperator.
BI Derivation of Some General Relations The Cartesian coordinates x y z of a vector r are related to its spherical polar coordinates. We have already defined the operators Xˆand Pˆ associated respectively to theposition and the momentum of a particle. L z XP y YP x.
In order to deal with this spin angular momentum a spin coordinate must be included in the wavefunction1 It is found that in these cases the quantum number j can then take on half-integer values as well ie j ¼0 1 21 3. X ypz zpy Ly zpx xpz 12 Lz xpy ypx. We find that the x-component of the angular momentum operator is given by and where is the z-component of the momentum operator and so on.
Angular momentum called spin angular momentum that cannot be described in terms of a spatial wavefunction c nxyz. So the formula for getting from the quantum number m to the z-component of angular momentum --- namely L_z mhbar --- isnt really a formula at all its basically just a definition. The total angular momentum of a system of such structureless point particles is then the vector sum L X X r p 52.
In other words quantum mechanically L x YP z ZP y. L y ih cos cot sin. Jk Σ i Jki where k labels x y and z and i labels the constituents whose angular momenta couple to produce J.
The system simply doesnt have a definite x- or y-component of angular momentum. Since angular momentum results from rotation about an axis it seems plausible that the mJ quantum number is related to the z-component of angular momentum.

Quantum Mechanics Of Angular Momentum Ppt Download
Orbital Angular Momentum In Three Dimensions
Ppt Orbital Angular Momentum Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 588278

16 Angular Momentum 1 Angular Momentum Operator 2
3 6 Orbital Angular Momentum Orbital Angular Momentum

Quantum Mechanics Of Angular Momentum Classical Angular Momentum

Quantum Mechanics Of Angular Momentum Classical Angular Momentum
Lesson Video Angular Momentum Nagwa

16 Angular Momentum 1 Angular Momentum Operator 2

Question Video Calculating The Angular Momentum Of A Solid Metal Sphere Nagwa

Left Panel Possible Spin Angular Momentum Combinations For Download Scientific Diagram

Quantum Mechanics Of Angular Momentum Classical Angular Momentum

Chapter 7 The Hydrogen Atom Orbital Angular Momentum

16 Angular Momentum 1 Angular Momentum Operator 2

Ppt Orbital Angular Momentum Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 588278

Chapter 7 The Hydrogen Atom Orbital Angular Momentum
Ppt Angular Momentum Of A Particle Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 1411102

Chapter 7 The Hydrogen Atom Orbital Angular Momentum

0 Comments